FAAの筆記試験(Knowledge Exam)について。 : Privateの筆記試験について : PVTの問題へ : IFR、筆記の解説 : IFR問題へ
Private Pilot : 2007年 Airman Knowledge Test Question (Written Exam)
551.
From which primary source should information be obtained regarding expected weather at the estimated time of arrival if your destination has no Terminal Forecast?
A) Low-Level Prognostic Chart.
B) Weather Depiction Chart.
C) Area Forecast.
552.
To best determine general forecast weather conditions over several states, the pilot should refer to
A) Aviation Area Forecasts.
B) Weather Depiction Charts.
C) Satellite Maps.
553.
(Refer to figure 16.) The Chicago FA forecast section is valid until the twenty-fifth at
A) 0800Z.
B) 1400Z.
C) 1945Z.
図16を見る
554.
What service should a pilot normally expect from an En Route Flight Advisory Service (EFAS) station?
A) Actual weather information and thunderstorm activity along the route.
B) Preferential routing and radar vectoring to circumnavigate severe weather.
C) Severe weather information, changes to flight plans, and receipt of routine position reports.
555.
To obtain a continuous transcribed weather briefing, including winds aloft and route forecasts for a cross-country flight, a pilot should monitor a
A) Transcribed Weather Broadcast (TWEB) on an NDB or a VOR facility.
B) VHF radio receiver tuned to an Automatic Terminal Information Service (ATIS) frequency.
C) regularly scheduled weather broadcast on a VOR frequency.
556.
(Refer to figure 16.) What sky condition and type obstructions to vision are forecast for upper Michigan in the western portions from 0200Z until 0500Z?
A) Ceiling becoming 1,000 feet overcast with visibility 3 to 5 statute miles in mist.
B) Ceiling becoming 1,000 feet overcast with visibility 3 to 5 nautical miles in mist.
C) Ceiling becoming 100 feet overcast with visibility 3 to 5 statue miles in mist.
図16を見る
557.
(Refer to figure 19, area E.) The top of the precipitation of the cell is
A) 16,000 feet AGL.
B) 16,000 feet MSL.
C) 25,000 feet MSL.
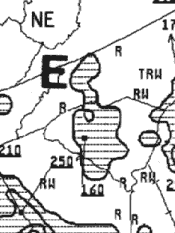 Figure 19, Area E
Figure 19, Area E
Figure 19を見る
558.
(Refer to figure 20.) How are Significant Weather Prognostic Charts best used by a pilot?
A) For overall planning at all altitudes.
B) For determining areas to avoid (freezing levels and turbulence).
C) For analyzing current frontal activity and cloud coverage.
和訳 と 解説
559.
(Refer to figure 20.) At what altitude is the freezing level over the middle of Florida on the 12-hour Significant Weather Prognostic Chart?
A) 4,000 feet.
B) 8,000 feet.
C) 12,000 feet.
和訳 と 解説
560.
(Refer to figure 20.) What weather is forecast for the Florida area just ahead of the stationary front during the first 12 hours?
A) Ceiling 1,000 to 3,000 feet and/or visibility 3 to 5 miles with continuous precipitation.
B) Ceiling 1,000 to 3,000 feet and/or visibility 3 to 5 miles with intermittent percipitation.
C) Ceiling less than 1,000 feet and/or visibility less than 3 miles with continuous precipitation.
和訳 と 解説
Florida州問題の説明
Private Pilot Knowledge Test (Private Written Exam) 05/23/2007 :
2008年の問題へ